Accidents that result in injury or trauma can occur to anyone. Understanding where your pain may have originated can assist you in getting back on your feet.
There are numerous ways to injure your back, ranging from minor strains that heal quickly to permanent injuries that cause severe chronic pain.
- Sprains and Strains
- Ligament Damage
What Are Strains and Sprains?
A long day at work, a sudden movement, or an injury can often cause a strain or sprain of the muscles and ligaments.
Most of the stress associated with bending, twisting, and lifting heavy objects is concentrated at the bottom of the spinal column, and this part of the back is especially vulnerable to injury, particularly in individuals with weak muscles who lead sedentary lifestyles.
What Causes Sprains and Strains?
A back strain occurs when the muscles surrounding the spine stretch too far, lift too much weight, or move in such a way that very small tears form. A small amount of bleeding into the muscle occurs due to the tearing of the muscles and ligaments, resulting in swelling and painful muscle spasms. The injured muscles are frequently tender to the touch. Pain and spasms are your body’s way of telling you that a muscle has been injured and needs to be restrained. As a result, you should avoid using the injured muscles during this period of acute pain and instead help them recover by resting, applying hot or cold packs, and possibly getting a gentle massage to help relieve spasms.
When you have a strained back, the actual damage done can vary greatly. The muscles that support and move the spinal column may be injured, the ligaments that connect the vertebral bodies or form strong capsules around the facet joints may be partially torn, or a mild slipped intervertebral disc may cause the pain. In each of these cases, the human body is usually capable of healing itself and will do so without surgery if the proper treatment is provided.
What Is the Treatment for Strains and Sprains?
Back strains and muscle spasms are prevalent, and there is no immediate cure for this type of injury. Most back strains, however, can be effectively treated with anti-inflammatory medications, a brief period of rest, icing at first, and then a gradual return to normal activities. A physical therapy program that includes stretching and strengthening exercises can help you heal and learn how to avoid future injuries. Using a TENS (transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation) machine may also be beneficial. Most of these treatments aim to reduce muscle spasms and pain so that you can resume your normal daily activities with minimal discomfort.
If you have mild back pain and believe you may have suffered a sprain or strain, non-surgical treatments can help your back heal. However, there are a few warning signs that you should consult a doctor about your back pain.
These are some examples:
- Weakness in your leg muscles, instability when walking, or a progressive decrease in the distance you can walk.
- Pain and numbness that travels down your legs, mainly when sneezing, coughing, or sitting down.
- Pain that wakes you up at night or worsens when you lie down
- Pain that is associated with fevers
- The pain associated with fevers
- Numbness in the buttocks, anus, or genital area
- Difficulty starting your urinary stream, inability to feel your urinary stream, or passing only small amounts
What if My Pain Continues Long After the Injury or Trauma?
Some injuries or trauma, such as falling down the stairs or slipping, can sometimes lead to pain that persists for several months—chronic pain. When conservative therapies like medication and physical therapy don’t help to relieve the pain, there are other treatment options to consider, such as back surgery and chronic pain therapies. Talk to your doctor if your pain doesn’t seem to go away.
What if my pain persists After the Injury or Trauma?
Some injuries or trauma, such as slipping or falling down the stairs, can result in pain that lasts for several months—chronic pain. When non-invasive treatments such as medication and physical therapy fail to relieve pain, there are other options to consider, such as back surgery and chronic pain therapies. If your pain does not seem to be going away, consult your doctor.
Ligament Injuries: What Are They?
Tendons are the connective tissue that connects muscles and bones. Ligaments are gristle-like tissues that surround joints and provide support. Lumbosacral strains or sprains can occur when a muscle in your back is overstretched or a ligament is torn. When this happens, the muscles in the injured area become immobilised, acting as a splint to protect the ligaments and joints from further damage.
Ligament injuries are usually caused by a traumatic event, and depending on the severity of the injury, they can take anywhere from six weeks to a year to heal. Many things can happen when a ligament is injured. The ligament can be strained, sprained, torn, or completely broken. Treatment options for these various types of injuries vary.
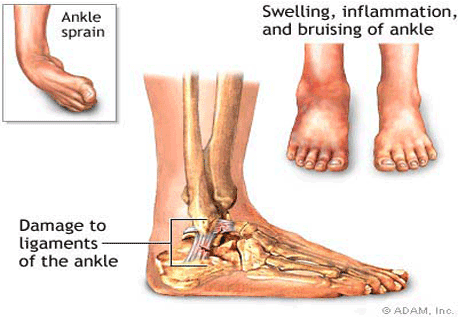
An accidental fall, twist, or slip can damage the ligaments that control your back joints, just as a sprain can damage the ligaments in your ankle. Sprained backs are caused by stretched and damaged pelvic ligaments.
Sprained backs are caused by stretched and damaged pelvic ligaments. The causes of back sprains and ankle sprains are very similar, and the treatment and recovery process can and should be the same. Firm pelvic ligament support will help to protect them from further strain while they heal and strengthen.
What Causes Back Ligament Injuries?
Poor posture can result in significant ligament damage. It is exhausting to stand for an extended period of time in situations such as waiting in line, standing at a party, or shopping. Many people will compensate for fatigue by slumping over without even realizing it. When we do this, our entire body begins to pull against the ligaments in the pelvis and lower back. Years of this can wear on the ligaments, causing them to become stretched and weakened, preventing them from properly controlling our joints. The simple strain of standing straight can cause discomfort and even pain.
